Introduction – Why Nox Sensors Matter in Modern Powertrains
In today’s industrial and automotive landscape, the demand for clean and efficient engines has never been greater. Businesses in manufacturing, logistics, and equipment production face mounting pressure to meet environmental regulations while maintaining performance and reliability. This is where the Nox sensor plays a crucial role.
A Nox sensor is a key component in modern engine control systems, continuously monitoring nitrogen oxide levels in the exhaust stream. For B2B buyers, such as OEMs, fleet managers, and equipment integrators, understanding how Nox sensors function is essential to selecting the right emission solutions that ensure compliance, longevity, and operational efficiency.
Understanding How Nox Sensors Work
A Nox sensor is typically installed in the exhaust system—either upstream or downstream of the catalytic converter—to measure the concentration of nitrogen oxides (NO and NO₂). These readings are transmitted to the engine control unit (ECU), which adjusts combustion parameters to maintain optimal air-fuel ratios and reduce harmful emissions.
Core Components and Operational Principles
At the heart of every Nox sensor is an electrochemical sensing element that detects oxygen and nitrogen oxides in real time. The sensor’s internal cells convert the gas concentration into an electrical signal, enabling precise monitoring of combustion efficiency. This feedback loop allows the ECU to fine-tune engine operation, improving fuel economy and emission control.
For example, in heavy-duty applications, reliable sensors are vital to achieving consistent performance across multiple operating conditions. High-quality sensors ensure long-term stability, fast response times, and accurate data interpretation. Many OEMs source Nox Sensor For Mercedes-Benz vehicles designed for integration with advanced exhaust systems, where precision and durability directly impact emission compliance.
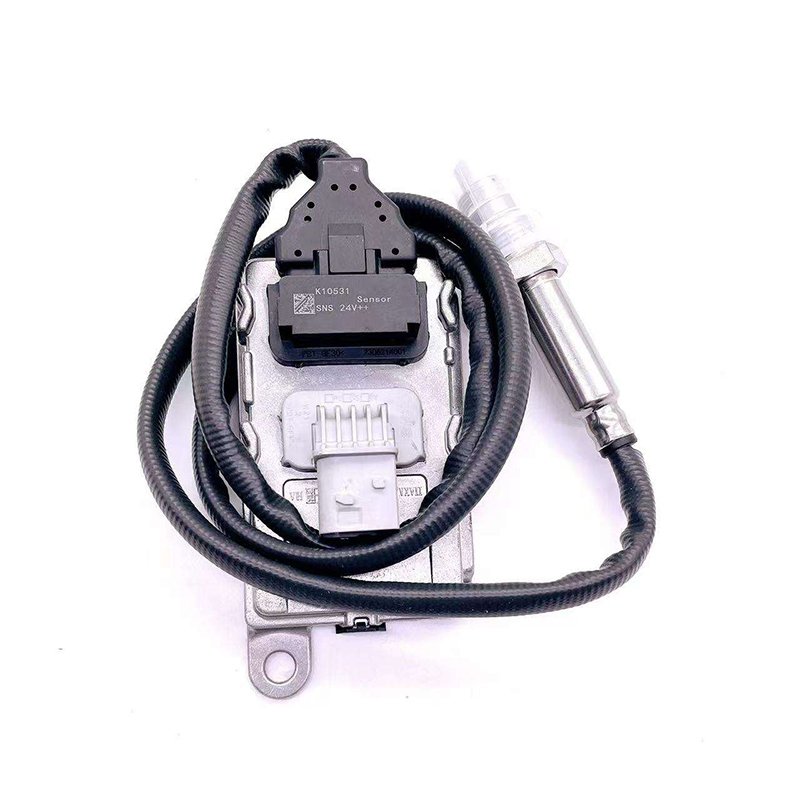

Nox Sensors in Emission Control Systems
Nox sensors form the backbone of emission control systems, particularly those using Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) or Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR). These systems rely on continuous feedback from the sensor to determine the correct amount of urea or exhaust gas to recirculate, ensuring optimal emission reduction and engine efficiency.
For B2B sectors such as industrial machinery and commercial vehicles, the ability to maintain consistent emission levels translates into operational stability and lower maintenance costs. Accurate sensor data helps prevent overuse of reductants and protects aftertreatment components from unnecessary wear.
Integration with Engine Management Systems
When integrated properly, Nox sensors communicate seamlessly with the engine management system. This interaction enables automatic adjustment of air-fuel ratios, injection timing, and aftertreatment dosing. The result is a system that adapts dynamically to varying loads and temperatures, maintaining compliance without sacrificing performance.
In the commercial vehicle sector, for instance, suppliers often provide Nox Sensor For Cummins engines, which are widely used in trucks, construction machinery, and generators. These sensors are built to withstand demanding conditions, supporting high-efficiency SCR systems and ensuring that emission thresholds remain within regulated limits.
The Role of Nox Sensors in Regulatory Compliance and Sustainability
As environmental standards become stricter worldwide, emission monitoring has become a fundamental part of corporate responsibility. Nox sensors enable companies to align with global emission regulations while enhancing the sustainability of their engine systems.
For B2B clients, reliable sensors are more than just compliance tools—they are long-term assets that protect engine components and reduce downtime. By providing real-time emission data, Nox sensors support predictive maintenance strategies, allowing manufacturers and fleet operators to make data-driven decisions that improve both efficiency and environmental performance.
Businesses that integrate robust Nox sensing technologies into their systems position themselves as forward-thinking partners in a greener industrial supply chain.
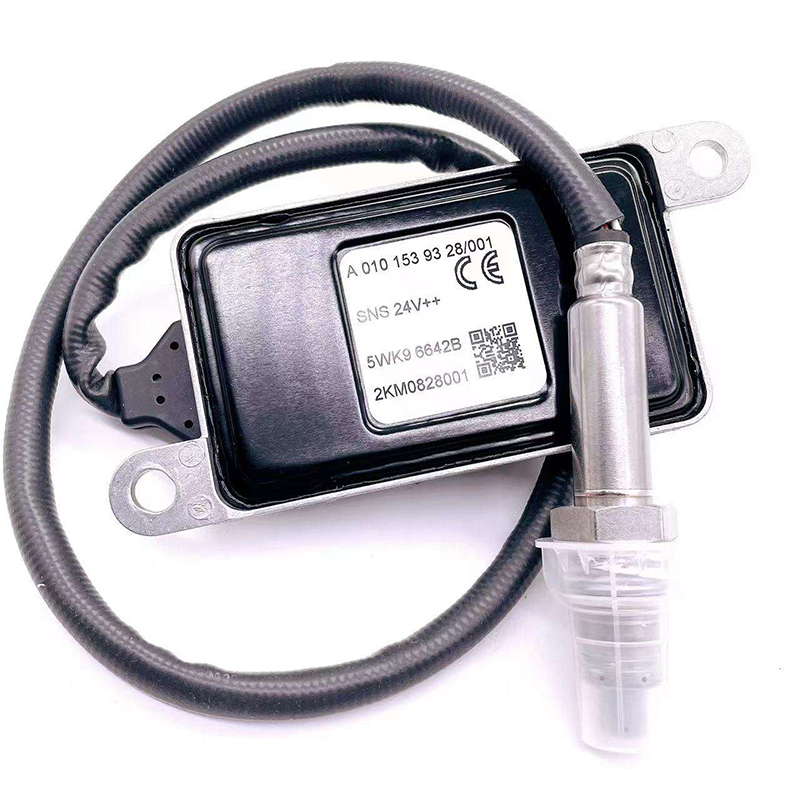

Choosing the Right Nox Sensor for Your System
Selecting the appropriate Nox sensor depends on factors such as system compatibility, signal stability, and integration ease. B2B buyers should look for suppliers with strong technical expertise and experience in engine management solutions.
While universal sensors exist, custom solutions often deliver better results, particularly in complex emission systems. Partnering with a manufacturer that understands your operational requirements ensures better calibration, improved longevity, and simplified installation. Whether your company operates in transportation, agriculture, or power generation, the right Nox sensor will enhance both performance and compliance.
Conclusion – Driving Cleaner Engines with Smarter Sensing
The Nox sensor has evolved from a regulatory necessity to a strategic component in emission system design. By delivering real-time feedback, supporting adaptive engine control, and improving aftertreatment performance, it empowers businesses to meet environmental goals without compromising productivity.
For manufacturers, distributors, and equipment suppliers, investing in high-quality Nox sensors is not just about meeting today’s standards—it’s about building the foundation for sustainable, future-ready engines. As global industries move toward cleaner technologies, the role of advanced sensing solutions will continue to expand, driving innovation across every sector of the engine and emission systems market.